TL;DR: LLMs have been traditionally regarded as sequential decoders, decoding one token after another. In this blog, we show pretrained LLMs can be easily taught to operate as efficient parallel decoders. We introduce Consistency Large Language Models (CLLMs), a new family of parallel decoders capable of reducing inference latency by efficiently decoding an $n$-token sequence per inference step. Our research shows this process – mimicking human cognitive process of forming complete sentences in mind before articulating word by word – can be effectively learned by simply finetuning pretrained LLMs. Specifically, CLLMs are trained to perform parallel decoding by mapping any randomly initialized $n$-token sequence to the same result yielded by autoregressive (AR) decoding in as few steps as possible. Experiment results show CLLMs obtained using our proposed method are highly effective, showing $2.4\times$ to $3.4\times$ improvements in generation speed, in par with or even beter than other fast inference techniques like Medusa2 and Eagle, yet require no additional memory cost to accomodate auxiliary model components at inference time.
CLLM
Consistency Large Language Models: A Family of Efficient Parallel Decoders
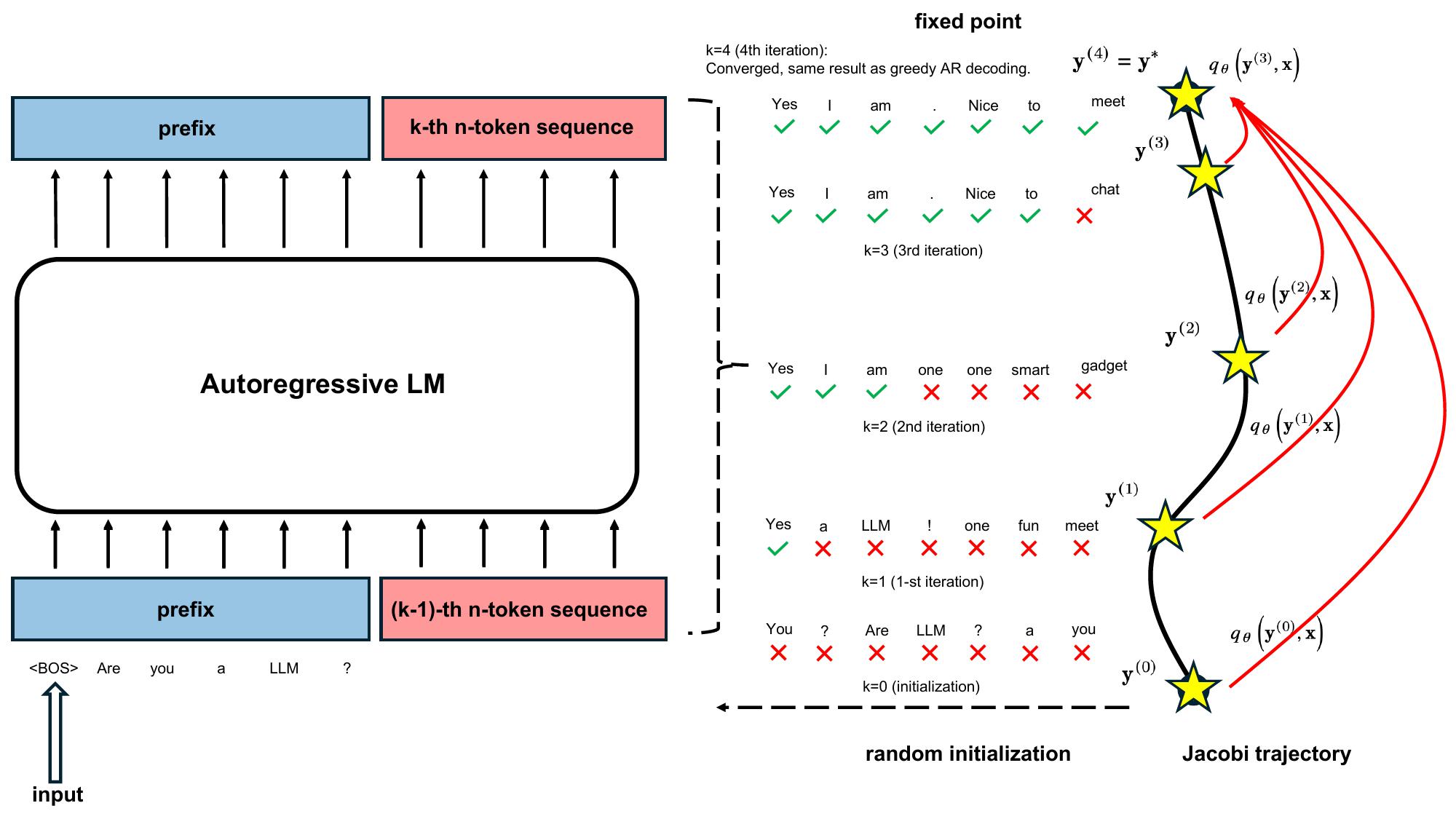
An instance of Jacobi trajectory and an illustration of the global consistency loss learning objective.

